Objective 3.1: Configure and Manage vSphere Distributed Switches (vDS)
Compare and contrast vDS capabilities
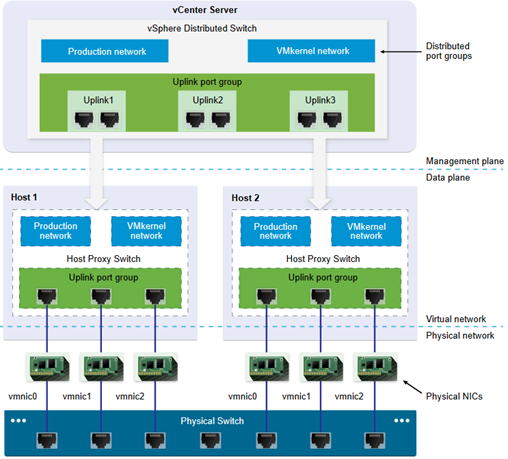
Provides centralized management and monitoring of the networking configuration of all hosts that are associated with the switch.
consists of two logical section:
- data plane implements the package switching, filtering,tagging, and so on
- management plane is the control structure that you use to configure the data plane functionality
In vSphere Standard Switch contains data plane and management plane individually. In vDS the data plane remains locally on every host that is associated with the distributed switch, and management plane is centralized per vCenter.
It’s composed by:
- Uplink port group (dvuplink)
- defined during vSwitch creation
- is a template that you use to configure physical connections of hosts as well as failover and load balancing policies
- At the host level, each physical NIC is connected to an uplink port with a particular ID
- Distributed port group:
- provide network connectivity to virtual machines and accommodate VMkernel traffic
- identify each distributed port group by using a network label
- It’s possible define NIC teaming, failover, load balancing, VLAN, security, traffic shaping , and other policies
Versions:
- Distributed Switch: 6.0.0 –> Compatible with ESXi 6.0 and later.
- Distributed Switch: 5.5.0 –> Compatible with ESXi 5.5 and later. Features released with later vSphere distributed switch versions are not supported.
- Distributed Switch: 5.1.0 –> Compatible with VMware ESXi 5.1 and later. Features released with later vSphere distributed switch versions are not supported.
- Distributed Switch: 5.0.0 –> Compatible with VMware ESXi 5.0 and later. Features released with later vSphere distributed switch versions are not supported.
Source:https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-vSphere/6.0/vsphere-esxi-vcenter-server-602-networking-guide.pdf
Create/Delete a vDS
- Create:
- In the navigator, right-click the data center and select Distributed Switch > New Distributed Switch
- In Name and Location, type a name for the new distributed switch, or accept the generated name, and click Next.
- Select version (see above)
- In Edit Settings configure the distributed switch settings:
- Number of uplinks
- NIOC
- Create a default port group
- Port group name, or accept the generated name
- In Ready to complete, review the settings you selected and click Finish
Source: https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-vSphere/6.0/vsphere-esxi-vcenter-server-602-networking-guide.pdf
Add/Remove ESXi hosts from a vDS and Add/Remove uplink adapters to dvUplinkgroups
- Add:
- Prerequisites:
- Verify that enough uplinks are available on the distributed switch to assign to the physical NICs that you want to connect to the switch
- Verify that there is at least one distributed port group on the distributed switch
- Verify that the distributed port group have active uplinks configured in its teaming and failover policy
- Procedure:
- navigate to the distributed switch
- From the Actions menu, select Add and Manage Hosts
- Select Add hosts
- Click New hosts, select from the hosts in your data center, and click OK
- Select the tasks for configuring network adapters:
- From the On other switches/unclaimed list, select a physical NIC
- Click Assign uplink
- Select an uplink and click OK
- Configure VMkernel adapters
- Select a VMkernel adapter and click Assign port group
- Select a distributed port group and click OK
- Impact level (referred to iSCSI traffic):
- No impact –> iSCSI continue normal function after new config is applied
- Important impact –> iSCSI function might be disrupted
- Critical impact –> iSCSI function will be interrupted
- Configure VM networking:
- To connect all network adapters of a virtual machine to a distributed port group, select the virtual machine, or select an individual network adapter to connect only that adapter
- Click assign port group
- Select dvPortGroup and click OK
- Prerequisites:
- Delete: Before you remove hosts from a distributed switch, you must migrate the network adapters that are in use to a different switch
- To add hosts to a different distributed switch, you can use the Add and Manage Hosts wizard to migrate the network adapters on the hosts to the new switch all together.
- To migrate host networking to standard switches, you must migrate the network adapters on stages
Source: https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-vSphere/6.0/vsphere-esxi-vcenter-server-602-networking-guide.pdf
Edit general vSphere vDS settings
General settings for a vSphere Distributed Switch include the switch name and number of uplinks:
- Procedure:
- navigate to the distributed switch
- Manage tab –> Settings –> Properties
- Click Edit
- Click General to edit the vSphere Distributed Switch settings:
- Name+
- Number of uplinks
- Number of ports
- NIOC
- Description
- MTU (Bytes)
- Multicast filtering mode:
- Basic –> forwards traffic related to a multicast group based on MAC address (last 23 bits of IPv4 address of the group)
- IGMP/MLD snooping –> forwards multicast traffic to VM according to IPv4 IPv6 addresses subscribed in multicast group (using Internet Group Management Protocol IGMP or Multicast Listener Discovery protocol MLD)
- Discovery protocol:
- LLDP or CDP
- Set to Listen, Advice or Both
- Administrator Contact
Source: https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-vSphere/6.0/vsphere-esxi-vcenter-server-602-networking-guide.pdf
Add/Configure/Remove dvPortgroups
A distributed port group specifies port configuration options for each member port on a vSphere distributed switch. Distributed port groups define how a connection is made to a network.
Procedure:
- Right-click the distributed switch and select Distributed port group > New distributed port group.
- type the name of the new distributed port group, or accept the generated name, and click Next
- Configure Settings
- Port binding:
- Static –> assign a port to a virtual machine vnic when is connected
- Dynamic Binding –> assign a port to virtual machine vnic when virtual machine is powered on
- Ephemeral –> No port binding. You can assign a virtual machine to a distributed port group with ephemeral port binding also when connected to the host.
- Port allocation
- Elastic
- Fixed
- Number of ports
- Network resource pool
- VLAN
- None
- VLAN –> Id 1 up to 4094
- VLAN Trunking –> a VLAN range
- Private VLAN
- Advanced –> it is possible customize the policy configuration
- Port binding:
- Configure Security
- Promiscuous mode
- MAC address change
- Forget Transmit
- Traffic Shaping
- Status
- Average Bandwidth
- Peak Bandwidth
- Burst Size
- Teaming and Failover
- Load Balancing
- Route based on originating virtual port
- Route based on IP hash
- Route based on source MAC hash
- Route based physical NIC load
- Network failover detection
- Link status only
- Beacon Probing
- Notify switches
- Failback
- Failover order
- Active uplinks
- Standby uplinks
- Unused uplinks
- Load Balancing
- Monitoring
- Netflow (enabled/disabled) –> provides the ability to collect IP network traffic as it enters or exits an interface. By analyzing the data provided by NetFlow, a network administrator can determine things such as the source and destination of traffic, class of service, and the causes of congestion.
- Miscellaneous:
- shuts down all ports in the port group (Yes/No)
- Additional settings
- Add description and set port policy override
Source: https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-vSphere/6.0/vsphere-esxi-vcenter-server-602-networking-guide.pdf
Configure dvPort settings
Change general distributed port settings such as the port name and description. Procedure:
- Locate a distributed port group in the vSphere Web Client.
- Select a distributed switch and click the Related Objects tab.
- Click Distributed Port Groups.
- Select a distributed port group
- Click the Manage tab, and click Ports
- Select distributed port from table
- Edit distributed port settings
- If override enable:
- Override port policies
- Configure reset at disconnect (discards any per-port override)
Source: https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-vSphere/6.0/vsphere-esxi-vcenter-server-602-networking-guide.pdf
Create/Configure/Remove virtual adapters
Network virtual adapter supported type:
- E1000E: Emulated version of the Intel 82574 Gigabit Ethernet NIC
- E1000: Emulated version of the Intel 82545EM Gigabit Ethernet NIC, with drivers available in most newer guest operating systems
- Flexible: Identifies itself as a Vlance adapter when a virtual machine boots, but initializes itself and functions as either a Vlance or a VMXNET adapter, depending on which driver initializes it
- Vlance: Emulated version of the AMD 79C970 PCnet32 LANCE NIC, an older 10 Mbps NIC with drivers available in 32-bit legacy guest operating systems
- VMXNET: Optimized for performance in a virtual machine and has no physical counterpart
- VMXNET 2 (Enhanced): Based on the VMXNET adapter but provides high-performance features commonly used on modern networks, such as jumbo frames and hardware offloads
- VMXNET 3 : A paravirtualized NIC designed for performance –> add multiqueue support , IPv6 offload, MSI/MSI-X interrupt delivery (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Message_Signaled_Interrupts)
- PVRDMA: A paravirtualized NIC that supports remote direct memory access (RDMA) between virtual machines through the OFED verbs API
- SR-IOV passthrough: Representation of a virtual function (VF) on a physical NIC with SR-IOV support
Add:
- Required privileges: Network > Assign network on a network.
- Procedure:
- Right-click a virtual machine in the inventory and select Edit Settings
- From the New device drop-down menu, select Network and click Add
- Expand New Network, and change the Status settings
- Connected
- Connected at power on
- Select the network adapter type to use from the Adapter Type drop-down menu
- Select how to assign the MAC address from the drop-down menu
- Automatic
- Manual
- From the drop-down menu next to the New Network label, select the standard or distributed port group to connect to
- If the network adapter is connected to a distributed port group of a distributed switch that has vSphere Network I/O Control version 3 enabled, allocate bandwidth to the adapter
- Shares
- Reservation
- Limit
Change:
- Required privileges: Network > Assign network on a network if you are changing the network the virtual machine connects to
- Procedure:
- Right-click a virtual machine in the inventory and select Edit Settings
- On the Virtual Hardware tab, expand Network adapter, and select the port group to connect to from the drop-down menu
- Change Status:
- Connected
- Connected at power on
- Select the network adapter type to use from the Adapter Type drop-down menu
- Select how to assign the MAC address from the drop-down menu
- Automatic
- Manual
- If the network adapter is connected to a distributed port group of a distributed switch that has vSphere Network I/O Control version 3 enabled, allocate bandwidth to the adapter
- Shares
- Reservation
- Limit
Migrate virtual machines to/from a vDS
In addition to connecting virtual machines to a distributed switch at the individual virtual machine level, you can migrate a group of virtual machines between a vSphere Distributed Switch network and a vSphere Standard Switch network.
Procedure:
- navigate to a data center
- Right-click the data center in the navigator and select Migrate VM to Another Network
- Select source network
- Select Specific network and use the Browse button to select a specific source network
- Select No network to migrate all virtual machine network adapters that are not connected to any other network
- Use Browse to select a destination network and click Next
- Select virtual machines from the list to migrate from the source network to the destination network and click Next
Source: https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-vSphere/6.0/vsphere-esxi-vcenter-server-602-networking-guide.pdf
Monitor dvPort state
vSphere can monitor distributed ports and provide information about the current state and runtime statistics of each port.
Procedure:
- Locate a distributed port group in the vSphere Web Client
- Select distributed port group
- Click Manage tab –> Ports
- Click start Monitoring Port State. Are displayed the following state:
- Link up
- Link down
- Blocked
- Unavailable (-)
Source: https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-vSphere/6.0/vsphere-esxi-vcenter-server-602-networking-guide.pdf
Determine use cases for a vDS
There are some use case that justify the use of vDS:
- Manage large environment: using dVS is possible to span switch modifications across multiple hosts using a single “action”.
- Ingress and Egress traffic shaping
- Private VLAN and VXLAN
- NIOC, Port mirroring and other advanced functionalities