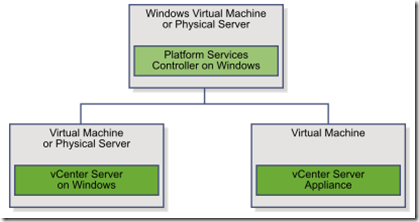
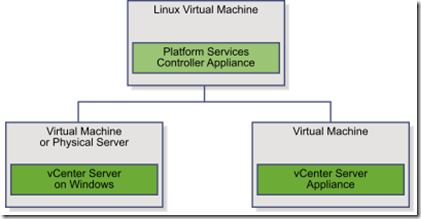
VCP 6 Study Note – vCenter Overview
vCenter is primary management tool for vSphere admins. It provides:
- point of control for all components in vDC
- management functionalities and services
- rights, permission and roles management
- storage and resource requirements management
- unification view of all resources provided by every ESXi host
Components in vCenter Server
- PSC (Platform Services Controller)
- Components and feartures:
- SSO
- Licensing
- certificate management
- RABC (role based access control)
- Could be installed:
- Deploy
- Windows vCenter (supports ipv4 and ipv6)
- vCenter Virtual Appliance (VCSA) (based on Linux VM Suse Ent 11 and supports ipv4 and ipv6)
- Embedded with vCenter Server
- External with 1 or more vCenter
- Database:
- Embedded
- Postgres:
- vCenter Windows supports max 20 hosts and 200VMs
- VCSA supports max 1000 hosts and 10K VMs
- SQL Server
- Postgres:
- External
- Windows: SQL Server and Oracle
- Embedded: Oracle
- Databases SQL
- SQL Server >= 2008 R2 with ODBC 64bit DSN entry
- SQL Server 2012 with ODBC 64bit DSN entry
- SQL Server 2014 with ODBC 64bit DSN entry
- Oracle
- Oracle 11g with ODBC 64bit DSN entry
- Oracle 12c with ODBC 64bit DSN entry
- Embedded
- Deploy
- Components and feartures:
- vCenter Server itself
vCenter Server Deployment models
vCenter and PSC deployment models are:
- vCenter with embedded PSC
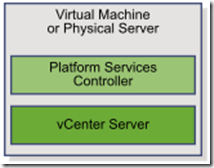
- advantages:
- The connection between vCenter Server and the Platform Services Controller is not over the network, and vCenter Server is not prone to outages because of connectivity and name resolution issues between vCenter Server and the Platform Services Controller.
- fewer Windows licenses on windows based installation
- fewer virtual machines or physical servers to manage
- do not need a load balancer to distribute the load across Platform Services Controller
- disadvantages:
- There is a Platform Services Controller for each product which might be more than required. This consumes more resources
- small scale environment.
- vCenter with external PSC
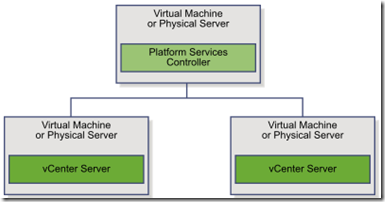
- advantages:
- Less resources consumed by the combined services in the Platform Services Controllers enables a reduced footprint and reduced maintenance
- more vCenter server instances in the environment
- disadvantages
- The connection between vCenter Server and Platform Services Controller is over the network and is prone to connectivity and name resolution issues
- need more Windows licenses in Windows based installation
- manage more virtual or physical server.
vCenter Server and PSC Requirements
Source:
Hardware requirements:
- PSC Only
- 2 vCPU
- 2 GB RAM
- Storage
- Program Files: 1GB
- Program Data: 2GB
- System folder: 1GB
- vCenter with int or ext PSC max 10Host 100VMs (tiny env)
- 2 vCPU
- 8 GB RAM
- Storage
- Program Files: 6GB
- Program Data: 8GB
- System folder: 3GB
- vCenter with int or ext PSC max 100Host 1000VMs (small env)
- 4 vCPU
- 16 GB RAM
- Storage
- Program Files: 6GB
- Program Data: 8GB
- System folder: 3GB
- vCenter with int or ext PSC max 400Host 4000VMs (mid env)
- 8 vCPU
- 24 GB RAM
- Storage
- Program Files: 6GB
- Program Data: 8GB
- System folder: 3GB
- vCenter with int or ext PSC max 100Host 1000VMs (large env)
- 16 vCPU
- 32 GB RAM
- Storage
- Program Files: 6GB
- Program Data: 8GB
- System folder: 3GB
Supported OS:
- Windows Server 2008 SP2 64bit
- Windows Server >= 2012
Check: KB 2091273 https://kb.vmware.com/selfservice/microsites/search.do?language=en_US&cmd=displayKC&externalId=2091273
VCSA Requirements
Hardware Requirements:
- VCSA + PSC
- max 10Host 100VMs (tiny env)
- vCPU: 2
- RAM: 8 GB
- Storage: 120GB
- max 100Host 1000VMs (small env)
- vCPU: 4
- RAM: 16GB
- Storage: 150GB
- max 400Host 4000VMs (mid env)
- vCPU: 8
- RAM: 24 GB
- Storage: 300GB
- max 100Host 1000VMs (large env)
- vCPU: 16
- RAM: 32 GB
- Storage: 450GB
- max 10Host 100VMs (tiny env)
- VCSA with external PSC
- max 10Host 100VMs (tiny env)
- vCPU: 2
- RAM: 8 GB
- Storage: 86GB
- max 100Host 1000VMs (small env)
- vCPU: 4
- RAM: 16GB
- Storage: 108GB
- max 400Host 4000VMs (mid env)
- vCPU: 8
- RAM: 24GB
- Storage: 220GB
- max 100Host 1000VMs (large env)
- vCPU: 16
- RAM: 32GB
- Storage: 280GB
- max 10Host 100VMs (tiny env)
- PSC Only
- supported environments
- max 10Host 100VMs (tiny env)
- max 100Host 1000VMs (small env)
- max 400Host 4000VMs (mid env)
- max 100Host 1000VMs (large env)
- Requirements:
- vCPU: 2
- RAM: 2GB
- Storage: 30GB
- supported environments
vCenter Server licenses and components
Common components:
- Management Service
- Provisioning
- Monitoring
- Configuring
- Configuration data
- Performance information
- inventory Service
- Web Client
- vCenter Server API
- .NET Extensions
- vCenter SSO
Licenses:
- Standard
- vCenter server orchestrator
- Linked Mode
- Enhanced Linked Mode (use same domain and site-name)
- Foundation
- Essential
Working ports
- SSO HTTPS port: 443
- HTTP port 80
- HTTPS port: 443
- Syslog service port: 514
- Syslog secure service port: 1514
- Auto Deploy management port: 6502
- Auto Deploy service port: 6501
- ESXi Dump collector port: 6500
- ESXi HB port: 902
- vSphere Web Client port: 9443